Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy – Report of two cases (Feb.2020)
Case 1
We report a case of laparoscopic management of Adrenal Angiolipoma of the right adrenal gland.
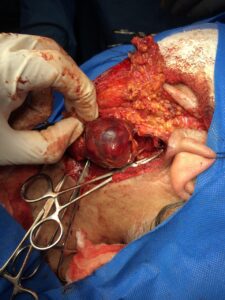
A 40-year-old male presented a 55 x 60-mm round, homogeneous, noninvasive fat-rich mass of the right adrenal gland. Hormone-activity values were within normal range. Provisional imaging diagnosis was ADRENAL MYELOLIPOMA. 4 ports laparoscopic right adrenalectomy done. The mass was removed laparoscopically along with the right adrenal gland, and its histopathologic evaluation was consistent with the features of ADRENAL ANGIOLIPOMA. Postoperatively, the patient presented no signs of fever or remarkable blood loss and was discharged on the 2nd postoperative day.
Laparoscopic Right Adrenalectomy for Right Adrenal Angiolipoma case of month february 2020
Case 2
28 year old female a known case of Cushing disease due to functioning left adrenal tumor. The patient was referred by the endocrinologist for laparoscopic left adrenalectomy.
The left adrenal mass was 7 * 6.5 cm hyper functioning well defined homogenous mass on ultrasound and CT scan of abdomen without calcification or necrosis. The patient prepared for surgery. 3 ports laparoscopic left adrenalectomy done with minimal blood loss. The histopathological result was consistent with ADENOMA. The postoperative course was smooth and the patient discharged on 2nd postoperative day.
Laparoscopic Left Adrenalectomy for Cortisol Secreting Adrenal Tumor case of month February 2020
Review of literature
Laparoscopic surgery in functional and nonfunctional adrenal tumors: A single-center experience
Author links open overlay panelBahadırÖzaAlperAkcanaErtanEmekaMuhammetAkyüzaErdoğanSözüeraHızırAkyıldızaAdnanBayrambRıdvanKuluaEnginOka
Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy (LA) is a safe and minimally invasive operation for benign adrenal tumours. The purpose of this study was a retrospective analysis of outcomes following laparoscopic lateral transabdominal adrenalectomy performed for benign adrenal tumours responsible for various endocrinological disorders and non-functioning tumours.
Methods
A total of 100 laparoscopic adrenalectomy were carried out between January 2007 and March 2013 via the lateral transabdominal approach. The analysed factors included demographic data of patients, indication for surgery, tumour size and side, intraoperative and postoperative outcome of laparoscopic lateral transabdominal adrenalectomy including duration of surgery, length of hospital stay, the complication rate, as well as the conversion rate to open adrenalectomy.
Results
There were 34 patients with non-functioning tumours (Group 1) and 66 with functioning tumours (Group 2). The intraoperative and postoperative outcomes were not significantly different in the cases among the analysed groups of patients. The median operative time was 101 ± 4.3 (range, 30–210) minute in group 1 and 95 ± 5.9 (range, 30–190) minute in group 2, there was not statistically significant (p = 0.56). The median duration of the postoperative hospital stay in the group 1 was bigger than group 2, this did not differ significantly (p = 0.08). Peroperative complications were occured in 9 (9%) patients, observing 6 (9%) patients in Group 1 and 3 (8.8%) patients in Group 2. There was not statistically significant (p = 0.96). In the postoperative period, three patients in group I, 1 patient in group II developed complications, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.69). The conversion to open surgery was found in 9 (9%) patients..
Conclusion
This study shows that laparoscopic lateral transabdominal adrenalectomy is a safe, effective, and technically feasible procedure in the treatment of both functioning and nonfunctioning benign tumours of the adrenal gland
Keywords: functioning adrenal tumoursnon-functioning adrenal tumourslaparoscopic lateral transabdominal adrenalectomy.