THE INCIDENTAL FINDING OF GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR IN PATIENT UNDERGOING LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY (Aug.2019)
Case presentation
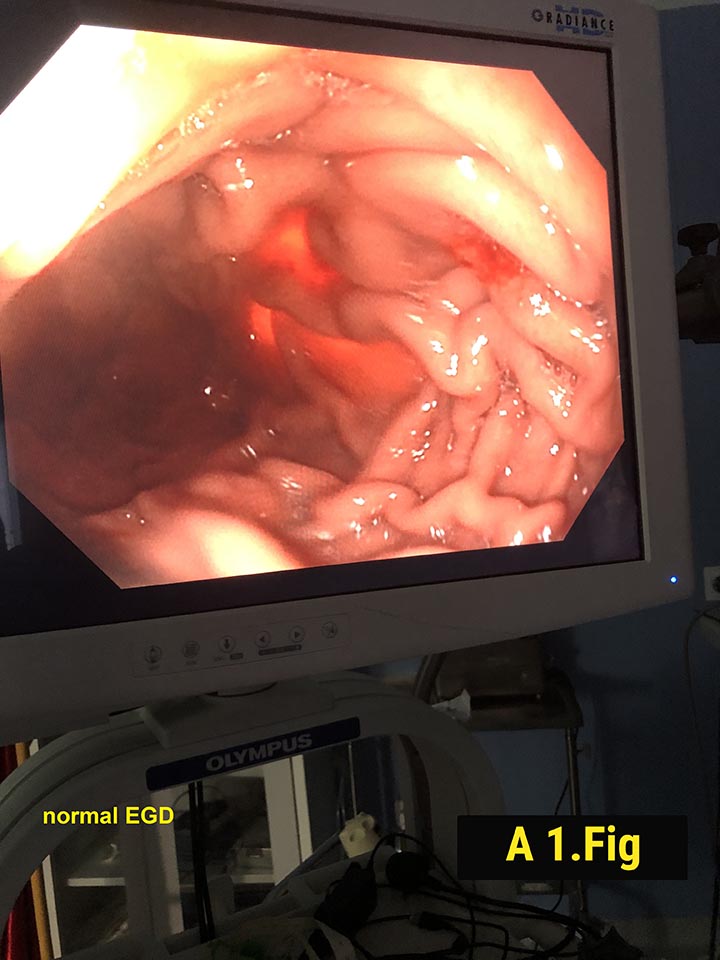
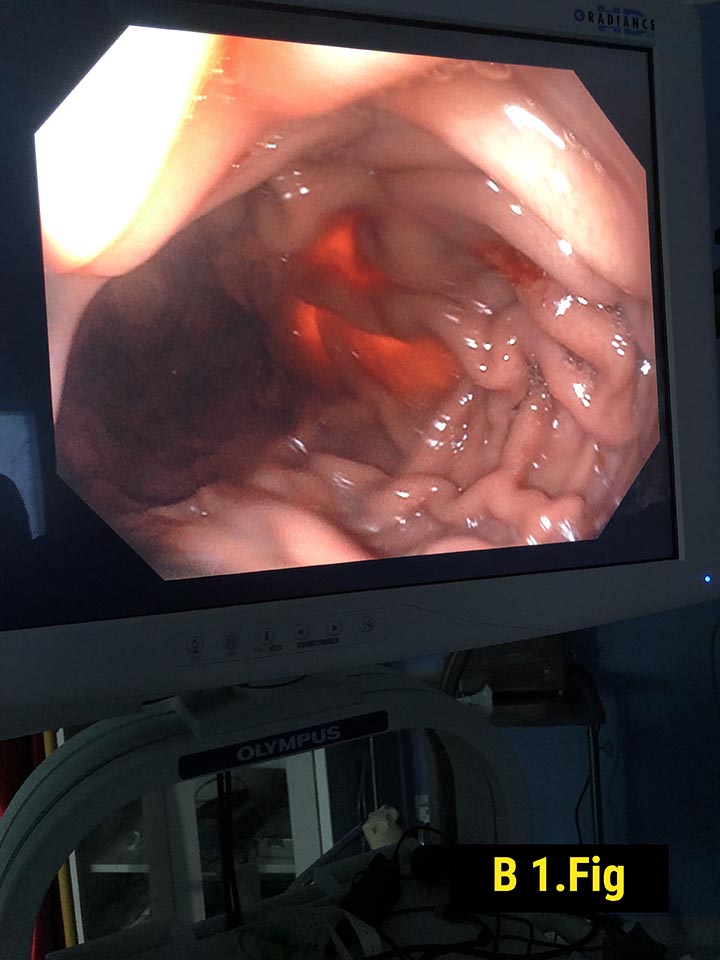
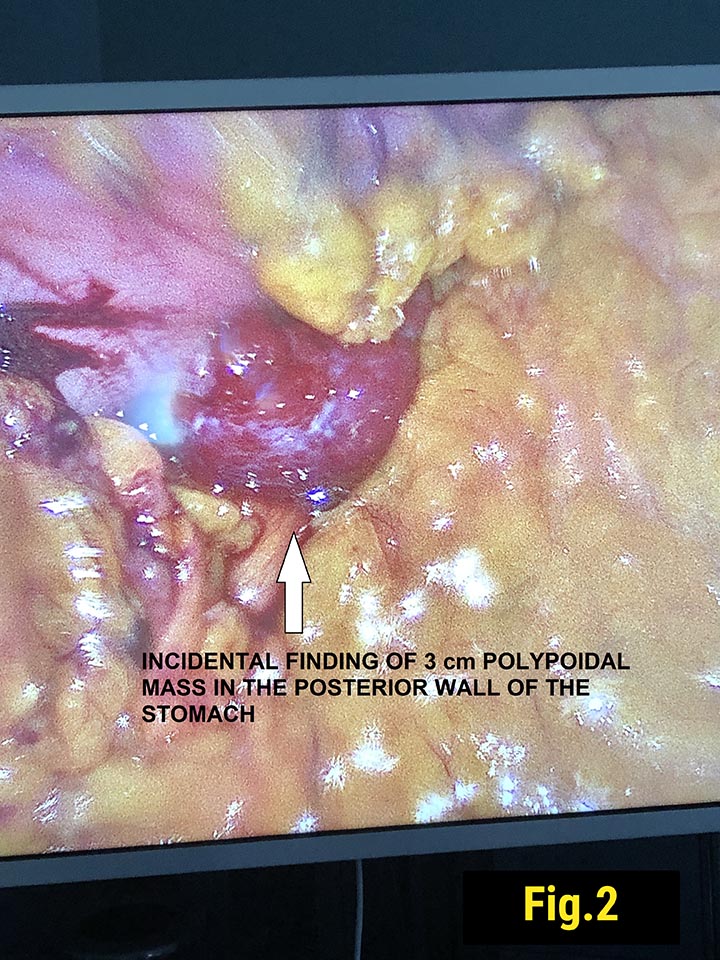
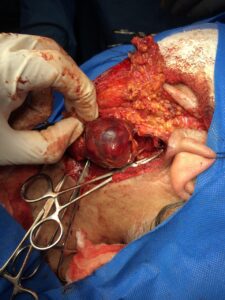
Forty ‐ one‐year‐old female with obesity (body mass index 40.2 kg/m2), hypertension, and sleep apnea underwent an elective laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. She had no symptoms suggesting the presence of a gastric tumor and preoperative upper endoscopy was normal (Fig.1). During surgery, a 3 cm polypoidal mass was found on the distal posterior surface of the stomach (Fig. 2).
Intraoperative esophagogastroscopy was done and it was normal.
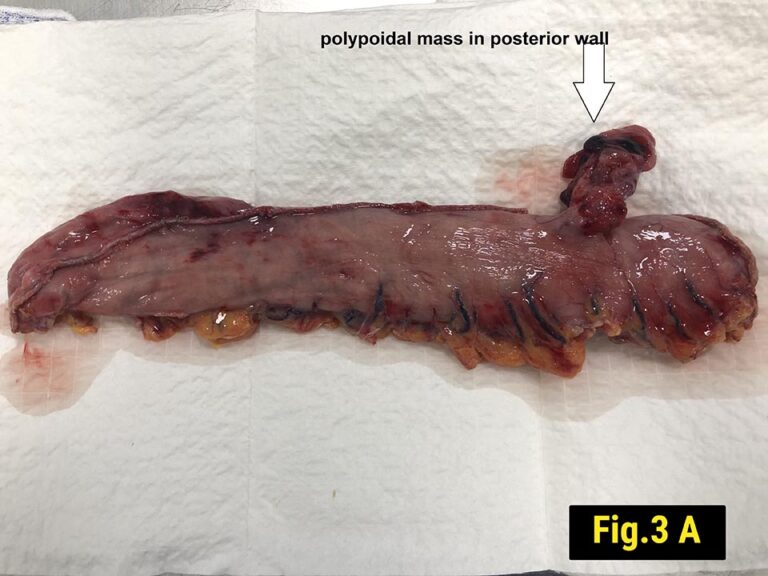
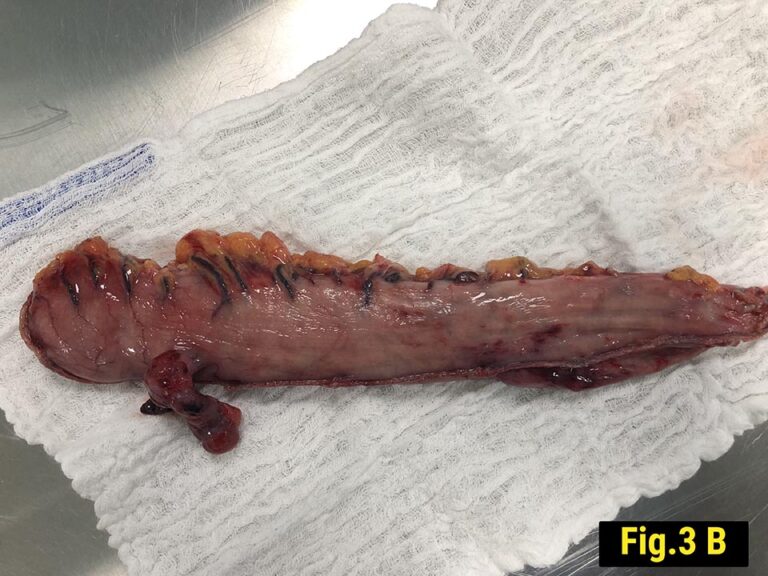
It was resected along with the gastric specimen, and histopathology showed epitheloid cells with relatively monotonus nuclei. (Fig.3)
Review of literature
THE INCIDENTAL FINDING OF GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMORS IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY: A CHART REVIEW FROM A HIGH-VOLUME BARIATRIC CENTER.
Dina Podolsky, MD1, Azam Qureshi, MD2, Mujjahid Abbas3, W. Scott Melvin, MD, FACS1, Diego Camacho, MD, FACS1. 1Montefiore Medical Center, 2Georgia Regents University, 3Louis Stokes VA Medical Center